Mosquitoes might be attracted to certain colours – new research
Cassandra Edmunds, Bournemouth University
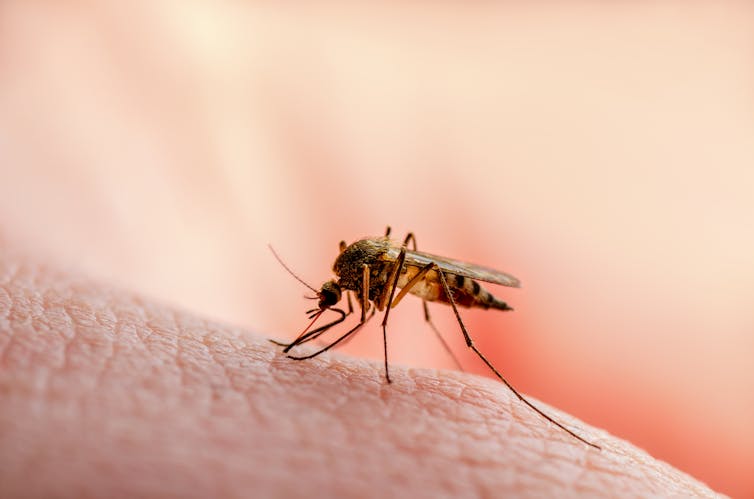
There’s no question that finding yourself covered in mosquito bites quickly takes the shine off a pleasant summer evening. But mosquitoes are more than a nuisance. They’re also the deadliest creatures on Earth, owing to the diseases they spread.
A lot of research on mosquitoes is dedicated to understanding their behaviour and preferences for who they bite. Vision is an important sense in biting insects, including mosquitoes. Although they don’t rely on their vision alone – smell and temperature work with visual cues to help mosquitoes locate a host.
Previous research has sought to link particular colours (or the wavelengths of light which we see as distinct colours) to mosquitoes’ host-seeking behaviour. However, the results have been mixed, with the same mosquito species showing preferences for different colours in different studies.
A recent study published in the journal Nature Communications is the latest to explore mosquitoes’ attraction to different colours. Could this research tell us how to avoid being bitten simply by adjusting the colours we wear? Let’s take a look.
The researchers conducted a series of experiments on three disease-spreading mosquito species: primarily Aedes aegypti, but also Anopheles stephensi and Culex quinquefasciatus.
In one experiment they used a wind tunnel equipped with cameras to track the mosquitoes’ flight patterns. The tunnel was designed to encourage them to behave as naturally as possible.
On the floor of the tunnel were two small coloured spots; one to represent the colour (wavelength) of interest and a control (white). Some of the colour samples were chosen to mimic different skin tones, including one to represent the colour of tanning lotion.
In mosquitoes, only the females bite, because in most species they require a blood meal to complete the reproductive process. So 50 mated but unfed female mosquitoes were released into the wind tunnel, where they would naturally search for a host.
After an hour carbon dioxide (CO₂) was released into the wind tunnel. CO₂ is exhaled by humans and other mammals. While it’s odourless to us, mosquitoes can smell it and use this scent to help guide them to a source of blood.
Seeing red
Before the odour stimulus was released, the Ae. aegypti mosquitoes largely ignored the coloured circles on the floor, instead exploring the ceiling and the walls of the tunnel. But once CO₂ had been introduced they started to investigate the coloured circles, particularly as the wavelength increased from 510 nanometres (nm) to 660nm.
These longer wavelengths represent colours in the orange and red end of the spectrum, though the Ae. aegypti mosquitoes were most attracted to the red, and then black. Notably, these orange to red wavelengths are the same as those given off from human skin tones. Blue, green and violet weren’t any more attractive to the mosquitoes than the control.
When the skin tone spots were used, they were more attractive to the mosquitoes than the control, but no preference was observed for any particular skin tone.
Previous experiments have shown mosquitoes are more attracted to contrasting colours, like a chequerboard pattern, than one solid colour. The researchers also showed the mosquitoes different spots against both similar and contrasting backgrounds. Ae. aegypti were more interested in spots with a high contrast to the background. Scientists believe this helps the mosquitoes distinguish between an object (person) and the background, even in low light. The contrast was more important in attracting the mosquitoes than the colour itself.
Similar to Ae. aegypti, An. stephensi were attracted to black and red, with little interest in the lower wavelengths. Cx. quinquefasciatus showed interest in violet/blue and red (interestingly, opposite ends of the tested spectrum).
The researchers conducted a separate experiment in insect cages to explore the mosquitoes’ attraction to real skin tones. Six volunteers from different ethnic backgrounds were recruited to help with this test. The control was a white glove in one window and the volunteers’ hands were held one at a time in the other window to see if the mosquitoes were attracted to any particular skin tone.
The mosquitoes were more attracted to the hands than the white glove, but as with the dots, there wasn’t a preference for a particular skin tone.
What does this all mean?
This study shows that mosquitoes are attracted to the colours found in human skin, but only in the presence of CO₂, suggesting the smell of human or mammal respiration may act as the initial cue. This confirms previous research which has found CO₂ attracts mosquitoes.
The researchers found that colour and contrast were important factors for Ae. aegypti who showed a preference for red, then black. An. Stephensi were interested in colours similar to Ae aegypti, though preferring black over red. Meanwhile, Cx. quinquefasciatus were interested in a range of colours.
As the researchers recognised, their experiments didn’t account for some of the other factors that affect mosquitoes’ choice of host. These include chemicals released from human skin, the temperature of the skin, and sweat on the skin. It would be interesting for future experiments to include these factors.
So what does this mean for the average person who doesn’t want to get bitten? You could try wearing white, blue or green and avoiding black, red and orange. Definitely avoid red and black checked patterns.
While adjusting your clothing may reduce your risk of being bitten, there’s no guarantee it will, or how effective this will be, particularly given the apparent variation in colour preferences between species. But these findings do suggest that with more research, colour could potentially be used as a tool in mosquito control.
![]()
Cassandra Edmunds, Lecturer in Forensic Biology, Bournemouth University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.




